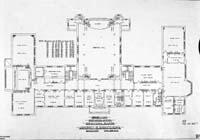
Original floor plans of the College Building. Notation: " Drawing no. 9 basement ventilation system; no. 10 ground floor ventilation system; no. 11 first floor ventilation system."
Bio/Historical Note: Designated as a provincial heritage property in 1982 and as a National Historic Site in 2001, the University of Saskatchewan's first building has long served as the architectural, intellectual and emotional cornerstone of the campus. Designed by Brown and Vallance, the College Building was originally intended ultimately to house the College of Agriculture; but from the start, served numerous purposes. As early as April 1910, the floor plan included space for milk testing, butter making, cheese making, grain work; a gymnasium; several classrooms; offices for the Registrar, Dean of Agriculture, Director of Extension, and President; the original "faculty club"; laboratories; the library; and quarters for the janitor. After a sod-turning ceremony on 4 May 1910, the cornerstone was laid by Prime Minister Wilfrid Laurier on 29 July 1910. It was constructed between 1910-1912 by Smith Bros. and Wilson general contractors. The building was officially opened by Walter Scott, Premier of Saskatchewan, on 1 May 1913. The College Building serves as a memorial to much of the university's history: numerous plaques to individuals and organizations can be found in its interior, including memorial ribbons honouring members of the university community who served in the First World War. In 1997 the university created "Nobel Plaza" in front of the College Building, honouring two Nobel Laureates associated with the University: Gerhard Herzberg and Henry Taube. As the university grew, the College Building gradually became the administrative centre for the university. By the 1950s most of the original teaching facilities were taken over by new or expanded offices including those of the registrar, controller, alumni and news services, and presidential staff. The building became known as the Administration Building at this point, and later the "old Administration Building" to distinguish it from the new wing. This expansion continued through the 1960s and 1970s, particularly with the appointment of a university secretary and vice-presidents. While Convocation Hall became too small for regular Convocation ceremonies by 1930, it maintained its original, broader function as a venue for concerts, meetings, lectures, and other events. Parts of the building were declared to be unsafe in 1979, which led to the construction of the new wing of the Administration Building, opened in 1987. Most of the original building was closed, but Convocation Hall remained in use until 1997. The building was reopened and officially rededicated as the College Building in September 2005 after a major rehabilitation project. The rehabilitation was reported to be "one of the largest heritage conservation projects in Canada - second only to the work being done on Parliament Hill." In addition to senior administrative offices and Convocation Hall, it became home to the Museum of Antiquities and new gallery space for the University Art Collection. Upon completion in 2012 the University Board of Governors renamed the Administration Building the Peter MacKinnon Building, in honour of Peter MacKinnon, retiring University President and a driving force behind the project.