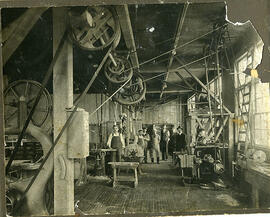
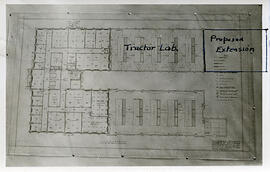
Architectural sketch of Engineering Building with proposed extension drawn in with pen.
Bio/Historical Note: The modern day Engineering Building was built on the foundations of the original Engineering Building which was destroyed by fire 13 March 1925. Construction began the following June with an expected completion date of 1 November 1926. Gentil J.K. Verbeke of Saskatoon designed the new building, which was initially budgeted at $277,150. In reality the project would run well into February 1926 and eventually cost $304,169.65. The still uncompleted Engineering Building was occupied by the college in January 1926. Similar in design to its predecessor, the new Engineering Building featured a few noteworthy improvements. These included skylights for the top floor and individual lights for the draughting tables, a smoking lounge for students, and a new library and reading room. The new building contained 89,000 gross square feet of space, and also housed the dean and assistant dean’s offices, about 15 staff offices, drafting rooms, several lecture rooms, laboratories and postgraduate student offices. In 1939 the west wing of the new building was extended northward to house the Mechanical Engineering laboratories and the welding shop. An extension of the tractor lab was completed on 7 February 1941 for $33,188.60. The extension was designed by Gentil J.K. Verbeke and was built by Shannon Bros. Construction. A full addition to the west wing also designed by Verbeke was completed in 1946 by W. C. Wells Contractors for $31,890. The official opening of the west wing took place on 10 February 1948. In 1949 a World War II Air Force hangar was adjoined to the building to provide “temporary” space for the college. In the fall of 1961 the Evan A. Hardy Laboratory was completed as part of greater construction on the building. The laboratory project included extensive space for the Department of Agricultural Engineering, the Agricultural Engineering Research and Development Section and the Divisions of Hydrology and Control Systems. The project was completed in 1963 for $611,761; it was constructed by W.C. Wells Construction. The lab was designed by architect J. K. Verbeke while the further addition was designed by the architectural firm of Webster, Forrester and Scott. In the late 1970s the Engineering Building would undergo drastic renovations.