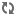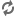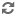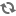- A-3009
- Item
- [1927 or 1928]
Progress shot of construction of the most westerly gate of the Memorial Gates. Thorvaldson (Chemistry) Building in background.
Bio/Historical Note: The Memorial Gates are a military memorial that is part of the University campus. Sixty-seven University students and faculty lost their lives while on service during World War I. The impact of the war on the University was immense: 330 students and faculty served during the War, a number equivalent to nearly all of the students who had registered the year prior to the beginning of the conflict. The desire to honor the staff and students who had fallen during the Great War was strong within the University community. As early as August 1918, 3 months prior to the formal Armistice, University President Walter C. Murray began making enquiries into the cost of a suitable memorial. What was settled upon were gates made of solid bronze, imported from England; the remainder, made of local greystone. Architect David R. Brown estimated the cost of what would come to be known as the Memorial Gates to be $30,000, with an additional $10,000 required for the memorial. The cement work was done by Richard J. Arrand in 1927-1928. A concerted fundraising effort among students and alumni helped cover the costs. The Memorial Gates were unveiled by President Murray and dedicated by the Bishop of Saskatchewan on 3 May 1928. A stone tablet, positioned between the bronze gates, bears the inscription: "These are they who went forth from this University to the Great War and gave their lives that we might live in freedom." For many years after, the site was used for the university’s Remembrance Day services at which wreaths are still laid every November 11th. These Gates were originally the entrance gates to campus and flanked University Drive. In the 1980s, due to increased traffic to the southwest portion of the campus, primarily Royal University Hospital, a new road entrance was built to the west. The gates remain, with the remnant of University Drive passing through them renamed Memorial Crescent. The gates are now primarily used by pedestrians, though the roadway is open to vehicles.