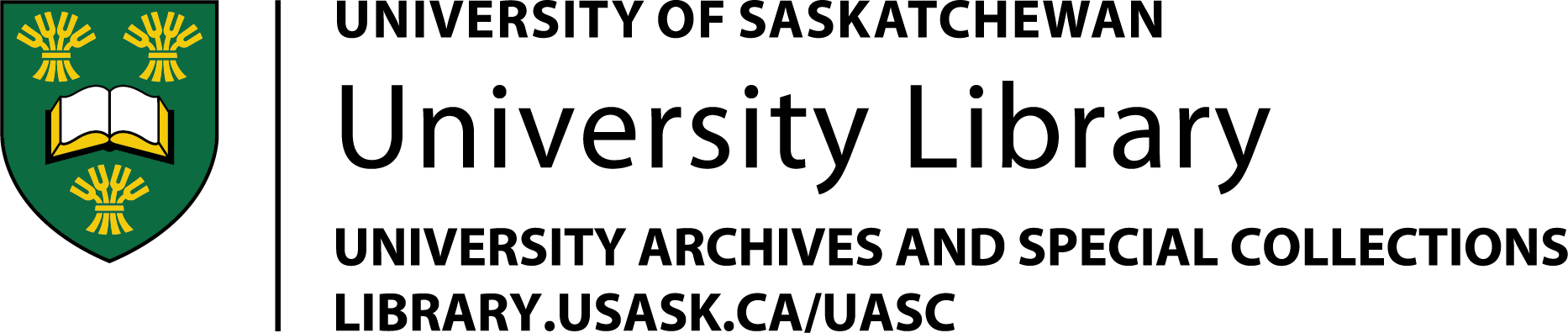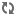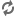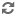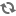Honourary Degrees - Presentation - Charles G. Power
- A-1788
- Stuk
- 17 May 1966
E.M. (Ted) Culliton, University Chancellor, making presentation of an honourary Doctor of Laws degree to Charles G. Power at Convocation in Physical Education gymnasium.
Bio/Historical Note: Charles Gavan (Chubby) Power was born in 1888 in Sillery, Quebec, He was educated at Loyola College and Laval University, graduating in law; while a student he was an outstanding athlete, and ultimately was a star with the Quebec Bulldogs of the Eastern Canada Amateur Hockey Association (ECAHA). A proficient scorer, he scored four goals in one game in 1908 and five goals in a game in 1909. Power served overseas in World War I, first as a captain and then as an acting major. He was wounded during the Battle of the Somme and was awarded the Military Cross for gallantry during military operations. Power entered politics in the 1917 federal election in which he was elected as a "Laurier Liberal" during the Conscription Crisis of 1917. In 1935, Power was appointed minister of pensions and health in the Liberal cabinet of Prime Minister William Lyon Mackenzie King. During World War II, he served as minister of national defence for air and was responsible for expanding the Royal Canadian Air Force. Power’s opposition to conscription led him to resign from the cabinet during the Conscription Crisis of 1944, after the government passed an Order in Council to send conscripts overseas. Power sat as an "Independent Liberal" for the duration of the war and was re-elected as an Independent Liberal in the 1945 federal election. He then rejoined the party and ran to succeed King in the 1948 Liberal leadership convention but came a poor third. Charles Power retired from the House of Commons in 1955. He was appointed to the Senate on 28 July 1955 and served until his death in Quebec City in 1968.