Summer School for Teachers - Qu'Appelle Valley
- A-4449
- Item
- Aug. 1965
From back of photo: "Teachers taking classes in school music methods and materials participate in one of the instrumental workshops. Instructor is Robert Bren." Students playing clarinets, trumpets, and flutes. held in the Qu'Appelle Valley, Saskatchewan.
Bio/Historical Note: The University Summer School emerged in 1914; for the first three years (1914-1917), the Department of Education assumed responsibility for the direction and support of the school. Only school teachers took the courses; these were designed to improve instruction in agriculture, household science, nature study, art, and elementary science. In 1917, at the request of the Department, the University took over management of the school, and classes were offered leading to a degree. Classes were given in English, Latin, Chemistry, Physics, and Field Husbandry. From 1919 to 1937, George H. Ling was Director; during his tenure it grew into one of the largest and best known university summer schools in Canada.

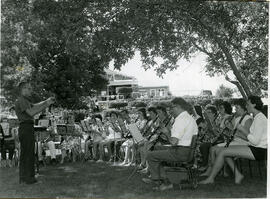



![Summer School for Teachers - [Qu'Appelle Valley]](/uploads/r/university-of-saskatchewan-archives/b/2/6/b2630fe7ae4b2891ba56be82165cc055dd295166361369ad3106e57565083878/A-4454_142.jpg)
