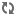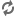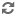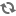- a-6805
- Pièce
- [ca. 1960]
Fait partie de University of Saskatchewan Photograph Collection
View of exterior of the Hangar Building.
Bio/Historical Note: The Hangar Building was originally constructed as a World War II Royal Canadian Air Force training facility at Dafoe, Saskatchewan. At a cost of $156,560, the hangar was dismantled and completely reassembled on campus by January 1947. It was intended to provide temporary teaching space for the Department of Household Science. The shingle clad wooden structure was built of post and beam construction on a concrete slab base, and many part-time students participated in its construction. It contained lecture rooms with seating space for 300, 200, 150, 125, 25 and 25 persons respectively, as well as three laboratories. Eight offices were also built for administrative staff so that offices on the ground floors of Qu’Appelle Hall and Saskatchewan Hall could be made available as residence space for returning veterans. While the Hangar Building had been designed to house the Department of Household Science the building was eventually occupied by the College of Commerce, while Household Science was relocated to the Physics Annex. Original intentions were to convert the building into a student curling rink after approximately five years. However such plans were abandoned by the mid-1950s in favour of a new curling facility located near Rutherford Rink, where it could share the existing ice-making plant. In 1967 the College of Commerce vacated the building to occupy the new Law-Commerce Complex, and the Department of Drama moved in. The Hangar Building thus became home to the Greystone Theatre. In September 1993 the Drama Department vacated the building to move into the recently renovated John Mitchell Building. The Hangar Building then remained unoccupied until its demolition in May 1994.