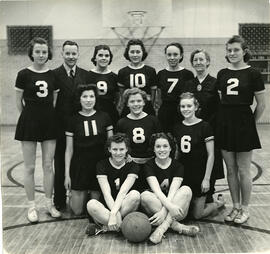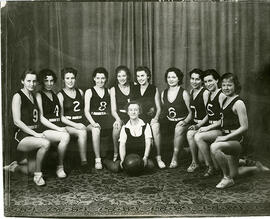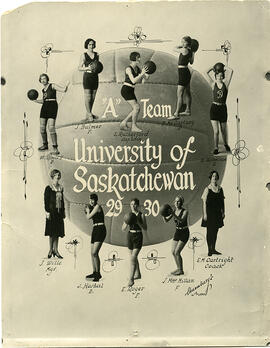Maureen Rever-Duwors - Portrait
- A-10739
- Item
- Nov. 1959
Head and shoulders image of Maureen Rever-Duwors, Assistant Professor, Department of Biology.
Bio/Historical Note: Maureen Rever-Duwors (born 1938) held provincial and Canadian records in sprint events as a high school student in the early 1950s at Luther College in Regina. She was Canadian champion in 1955 and the 60-and 100-yard events and coupled with a second place finish in broad jump and a third in the 220 yards, was the top point-getter among senior women at the meet. During Rever’s first year of university at Luther College, she competed in 100 metres (fifth in a heat), 200 metres (fifth in a heat) and the 4x100-metre relay at the 1956 Olympics in Melbourne, Australia. Rever enrolled at the University of Saskatchewan in 1956. While a student, she finished third in the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games 4×110 yards relay (with Diane Matheson, Eleanor Haslam (also from the University of Saskatchewan), and Freyda Berman). Rever was eliminated in the semi-finals of the 220 yards and in the heats of the 100 yards. Rever also played both guard and forward on the Huskiette basketball team. She was a member of the bronze-winning 4×100 metres relay team in the 1959 Pan American Games, and also finished fourth in long jump. Rever received a BA in 1959 and was the first woman on the Biology Department faculty (ca. 1970). Rever went on to become an official, administrator and internationally-rated official. She was an executive member of the Athletic Association of Canada, Saskatchewan Branch; a director of the Saskatoon Track and Field Club and was a founding member of Sask Sport. She was inducted into the Saskatchewan Sports Hall of Fame and Museum in 1977 and in the Saskatoon Sports Hall of Fame in 1986. Rever Road in Saskatoon is named in her honour. Rever is Professor Emerita of Biology (2021).