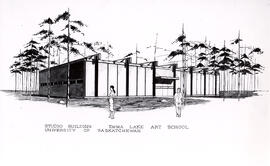
Emma Lake Art Studio - Architect's Sketch
- A-305
- Item
- [1937?]
Architect's sketch of the studio at Emma Lake Art School.
Bio/Historical Note: Artist workshops have been held at Emma Lake, Saskatchewan, since 1935. Augustus F. (Gus) Kenderdine, an artist trained at the Academie Julian in Paris and an instructor in the fledgling Department of Art at the University of Saskatchewan, established a summer art camp on an eleven-acre boreal forest peninsula on the shores of Emma Lake. In the early 1930s Kenderdine had purchased land at Murray Point on Emma Lake, and convinced Walter C. Murray, first president of the University of Saskatchewan, that a summer art camp could perform a vital role in the offerings of the department. In 1936 the Murray Point Art School at Emma Lake was officially incorporated as a summer school program. The school was also known as the art colony. Participants were teachers and artists who came from all over the province to learn how to teach art in Saskatchewan schools. After Kenderdine's death in 1947, a new generation of Saskatchewan artists came of age or moved into the province, including Kenneth Lochhead, Arthur McKay, Ronald Bloore, Ted Godwin, and Douglas Morton, popularly referred to as the Regina Five. In 1955 Lochhead, director of the Regina College School of Art, proposed a two-week workshop at Emma Lake to follow the Murray Point Art School classes. The workshop concept, based on modernist art, was established to keep Prairie artists in touch with art centers such as New York and Toronto. The internationally renowned Emma Lake Artists' Workshops became an established annual event and continued virtually unchanged until the last workshop was held in 1995. Since the mid-1960s the site has also been a provincial research area under the auspices of the U of S Department of Biology for biologists and other researchers. It is the most northerly field station in Saskatchewan and one of the few sites in Canada that specifically examines the boreal forest. It was declared as a game preserve in 1962. In 1989 the site was officially designated as Emma Lake Kenderdine Campus in recognition of Gus Kenderdine. The campus closed in 2012. In 2020 the university relocated nearly two dozen cabins at the site to Montreal Lake Cree Nation to provide additional housing during the COVID-19 pandemic.